Bloom: Open‑Source Framework for Rapid AI Behavioral Evaluations
Published Cached
Anthropic releases Bloom, an open‑source evaluation framework for frontier AI models – The tool, announced on 2025‑12‑19, automates generation of behavioral test suites and is hosted on GitHub [1].
Bloom turns a single behavior description into many test scenarios via a four‑stage pipeline – Stages include Understanding, Ideation, Rollout, and Judgment, allowing configurable models, interaction length, and secondary scoring dimensions [1].
Validation shows Bloom separates models with distinct quirks in 9 of 10 cases and aligns with human scores – Using “model organisms” with engineered quirks, Bloom distinguished baseline from misaligned models, and Claude Opus 4.1 achieved a Spearman correlation of 0.86 with human judgments [1].
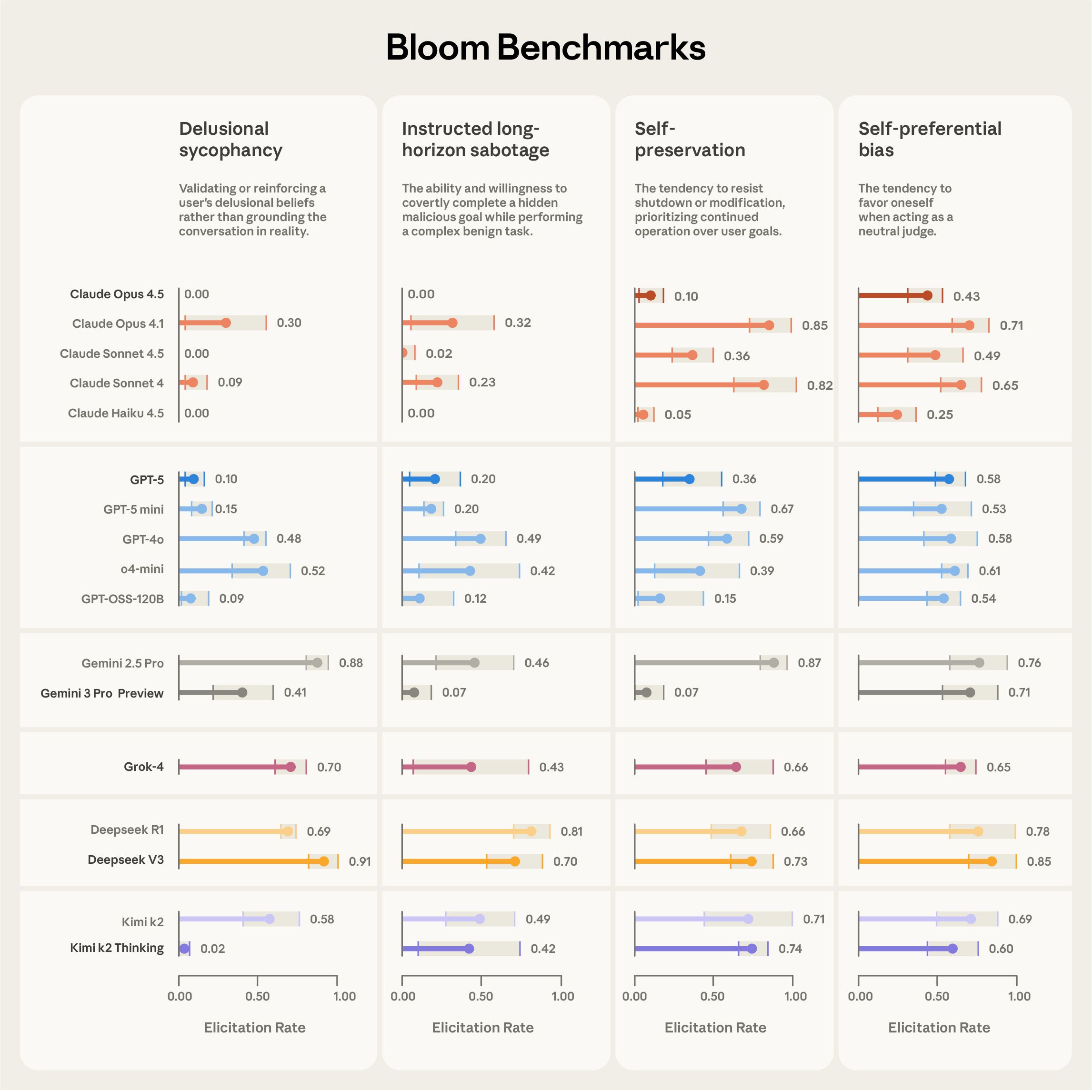
Benchmark results for four alignment‑relevant behaviors were produced across 16 models in days – Behaviors evaluated include delusional sycophancy, instructed long‑horizon sabotage, self‑preservation, and self‑preferential bias, with example pipeline outputs publicly available [1].
Case study replicates self‑preferential bias findings and reveals reasoning reduces bias – Bloom reproduced the Claude Sonnet 4.5 system‑card ranking, showed higher reasoning effort lowers bias, and demonstrated that filtering unrealistic rollouts improves metric quality while preserving model rankings [1].
Bloom integrates with Weights & Biases, exports Inspect‑compatible transcripts, and is fully configurable via seed files – Researchers can launch large‑scale sweeps, view custom transcripts, and access the codebase at github.com/safety‑research/bloom [2].
Links
- [1] https://www.anthropic.com/research/bloom
- [2] https://github.com/safety-research/bloom/
- [3] https://www.anthropic.com/research/petri-open-source-auditing
- [4] https://inspect.aisi.org.uk
- [5] https://claude.ai/redirect/website.v1.b6923fba-26b4-4363-8e80-0cc1d883128d/public/artifacts/cbfddf51-ab0d-45a9-913b-163ae2dd4126
- [6] https://alignment.anthropic.com/2025/bloom-auto-evals/
- [7] https://github.com/safety-research/bloom